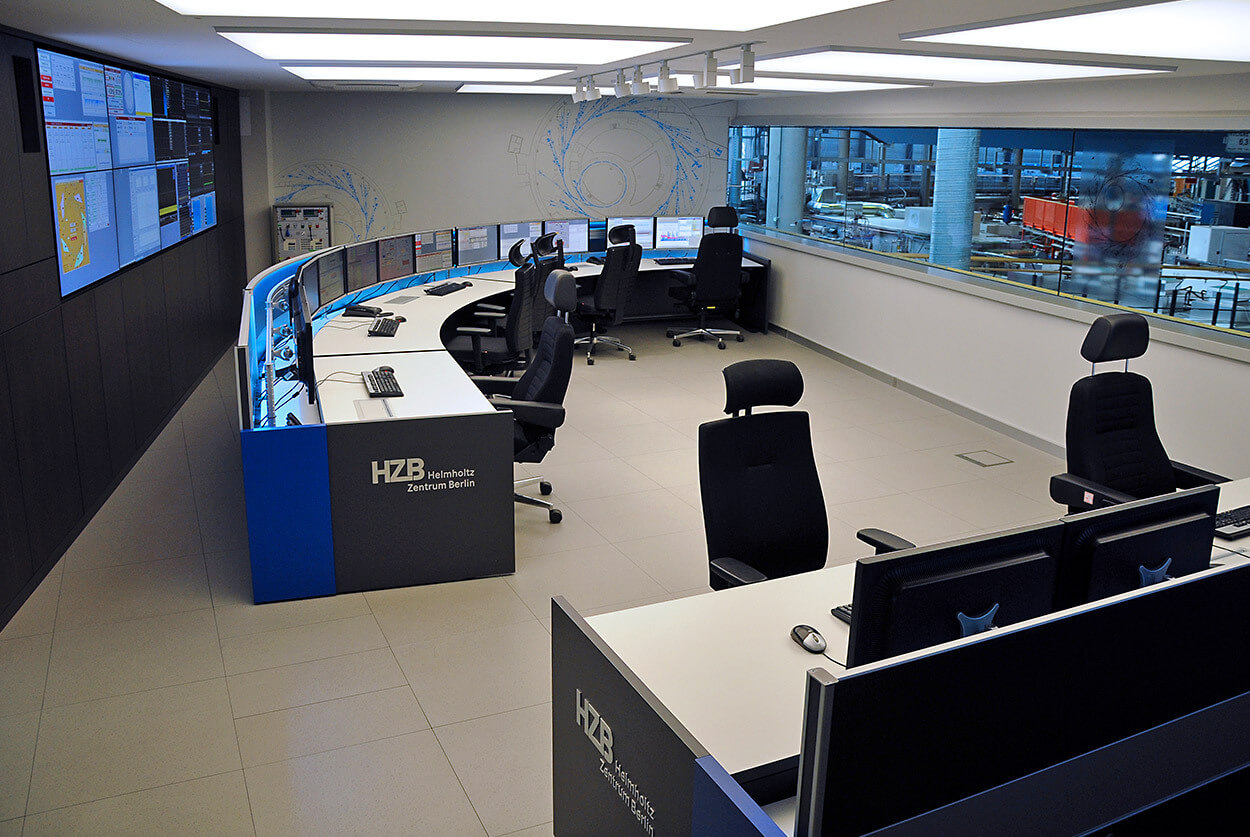
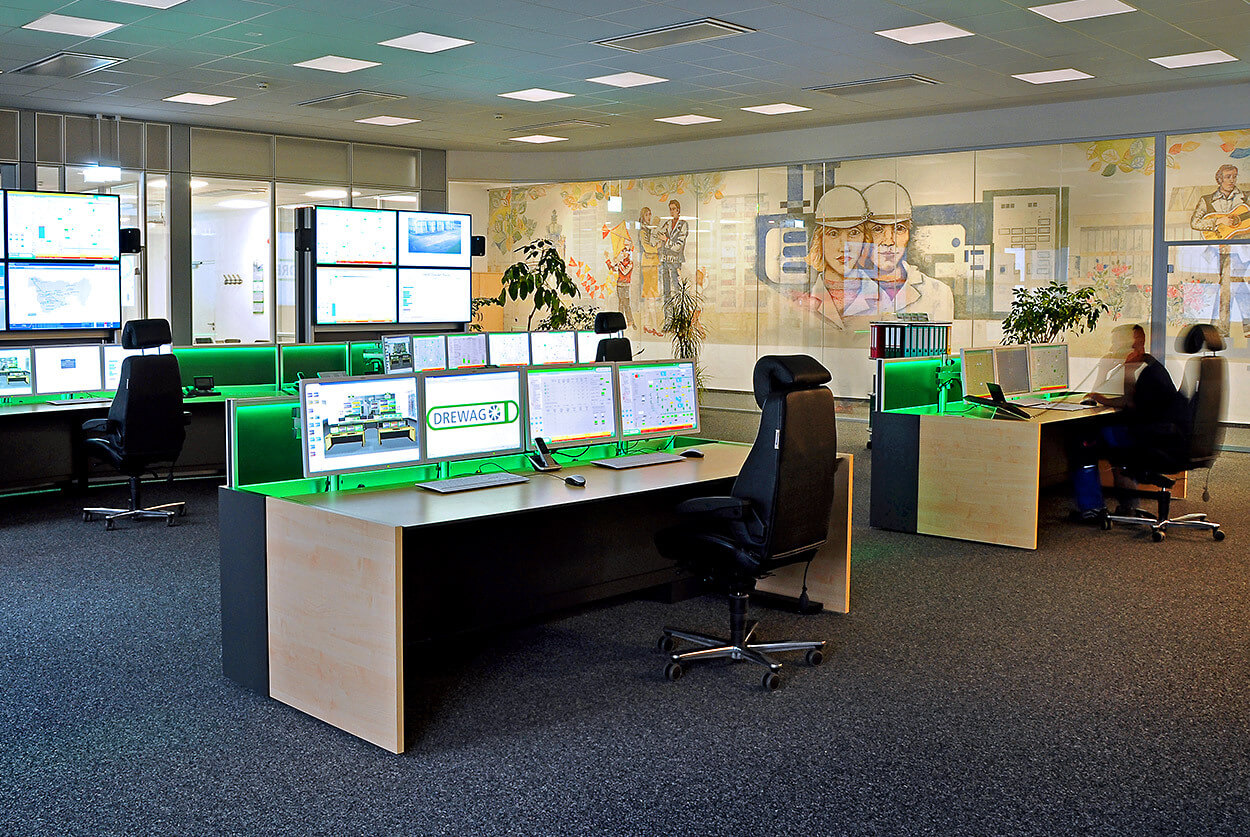
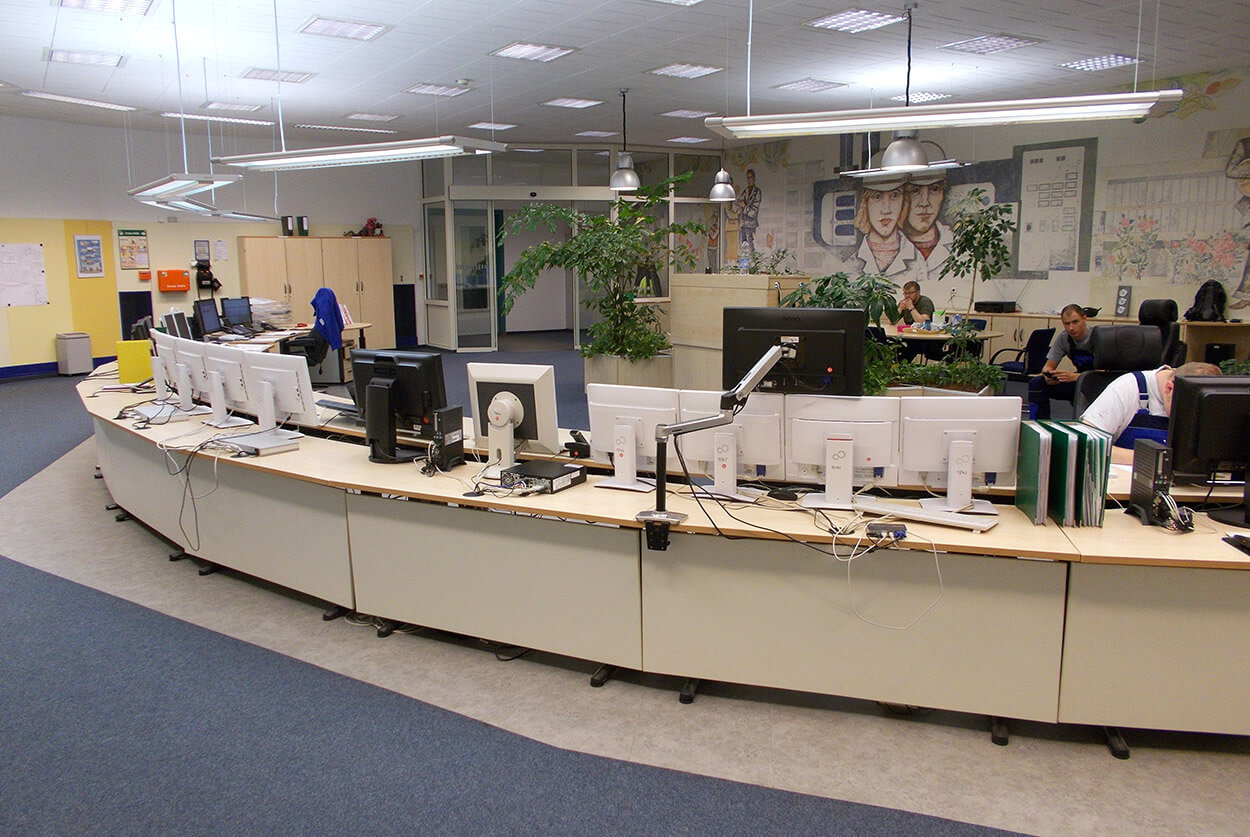
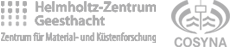Source: feedback from our customers from more than 500 implemented projects.
The future development of the control rooms
„Mission possible“: Aufbruch in eine neue Ära der Digitalisierung
Focus on forward-looking monitoring and control
Everyone is talking about the hype surrounding Big Data. Data is the new raw material. No company can escape the consequences of digitalization, the huge flood of data and its analysis. A phenomenon that forces the economy to react. New IT concepts and systems are required that enable the collection, use and exploitation of these rapidly growing volumes of data. The solution is highly efficient control rooms, whose importance will reach a completely new level in the coming years.
New challenges in control room equipment
For the JST specialists one thing is certain: With digitization and Industry 4.0 we are experiencing an unprecedented challenge in the discipline of control room equipment. The Jungmann Systemtechnik team has set out to roll up its sleeves and turn the control room landscape inside out, to cut off old pigtails and give the control room world a new face. Today, JST’s skilled and hand-picked employees help JST customers gain a competitive advantage as they move into a new era of digitalization via the control room.

Industrie 4.0: – the comprehensive digitalization of production
Production plants that are equipped with countless sensors and actuators for communication. Devices that exchange data and send status information in real time. Thanks to digitalization, gigantic amounts of data are produced. But this information only generates real added value when it is brought into a constructive relationship with one another, when trends can be derived from it and when it is available in a knowledge database in line with requirements, at the right time and in the right place for man and machine.
What does this mean for the control room?
All the threads of production come together in the control room – the perfect place to link the most important data. The work of the operators is supported by new IT systems that increase efficiency and performance in the production processes. This creates a completely new dimension in the IT infrastructure for monitoring and controlling all machines. The consequence, however, are new dependencies. Because this extraordinarily complex IT infrastructure must be operated with high availability – ideally monitored and controlled by an IT control room as IT Service Management (ITSM).
Get advice now!

Get advice now!
Internet of Things – when everything suddenly communicates, completely new possibilities develop
The Internet of Things (IoT) networks all objects for communication worldwide. With high bandwidths but also ultra-short and highly reliable response times, the 5G network will be a decisive driving force for the Internet of Things. An example from the consumer sector: the coffee machine equipped with IoT technology supplies consumer data to the manufacturer. When and where is which type of coffee brewed? The machine also asks for preferences: Which aroma is best received? This would enable the most popular varieties to be supplied in the required quantity at the right time. For which customer behavior or locations do the machines require faster descaling? Can specifications for the service be derived from this?
Since all devices could provide valuable data from practical experience, it will be possible to produce more in line with demand. Manufacturers will offer additional services as an additional business model (e.g. as an app) in order to gain advantages over competitors.
What does this mean for the control room?
New control rooms will be created that are not even conceivable today. Every sector benefits. No matter whether coffee roaster or steelworker: the possibilities are endless.
Discuss the future with JST now!

Discuss the future with JST now!
Artificial Intelligence – when the machine is smarter than the operator
What artificial intelligence can accomplish in the control room is illustrated by the example of a transport company that manages bus traffic in a large city: traffic jams, accidents, closures – diverting to alternative routes is part of daily business. This is where the “digital colleague” comes into play. As an artificial operator, an algorithm calculates the perfect diversion route for the bus from all available variables – more efficiently than a human could ever do.
What does this mean for the control room?
In the future, the operator will leave a large part of his decisions to the computer. In this way the human being is relieved, but also loses a significant area of his previous core competence. The original main task of monitoring and controlling a system is changing. At the same time, the new demands on the operator are a major challenge: learning, controlling and optimizing an artificial intelligence. This requires extensive knowledge. Continuing education is therefore the focus. A paradigm shift that offers new chances and possibilities, but which also raises a question: If the machine is smarter than the operator, who is responsible?
Get advice now!

Get advice now!
Machine Learning: – what machines can learn from machines
The term Machine Learning is based on the technical feasibility of IoT and Industry 4.0. Starting point: If all devices are networked and communicate with each other, you can also learn from each other. In concrete terms, this means that systems and plants exchange diagnostic data, even if they are distributed around the globe.
For example, a system detects that, at a certain temperature and humidity, faults in the production process occur repeatedly. By throttling the throughput speed, a failure can be avoided. This information is independently forwarded to other systems so that the necessary knowledge is globally available.
What does this mean for the control room?
In the control room the communication between the machines is monitored and controlled. Do the “experiences” exchanged by the machines make sense? Or should certain consequences be deliberately ignored? At this point the control room becomes the interface between plant operation and product development. The exchanged experience values of the machines can be incorporated into the product development and thus contribute to the continuous optimization process.
Lassen Sie sich jetzt beraten!
Lassen Sie sich jetzt beraten!
The digital factory and Smart Factory increased efficiency in real time
The term Industry 4.0, when looked at more closely, is equivalent to the realization of the requirements of the “Smart Factory”. The basis for the implementation, i.e. the pioneer of this intelligent, ideally self-organizing production environment, however, is the digital factory. It forms the data basis for the planning of factories in virtual reality (digital twin), which are subsequently implemented in so-called smart factories. Whether production plant or logistics system – with virtual production sites as a representation of the real world, intelligent networking should make it possible to optimize plants in shorter time cycles and lead to increased efficiency in real-time.
What does this mean for the control room?
The production adapts to the customer’s wishes. This continuous optimization implies that plants are subject to ever shorter innovation cycles. Plant-specific knowledge, which the employees in the control room or in the control center have acquired over many years, will fade into the background. The operator will have to be more adaptable. He is expected to keep pace with IT, less with the plant itself.
Get advice now!

Get advice now!
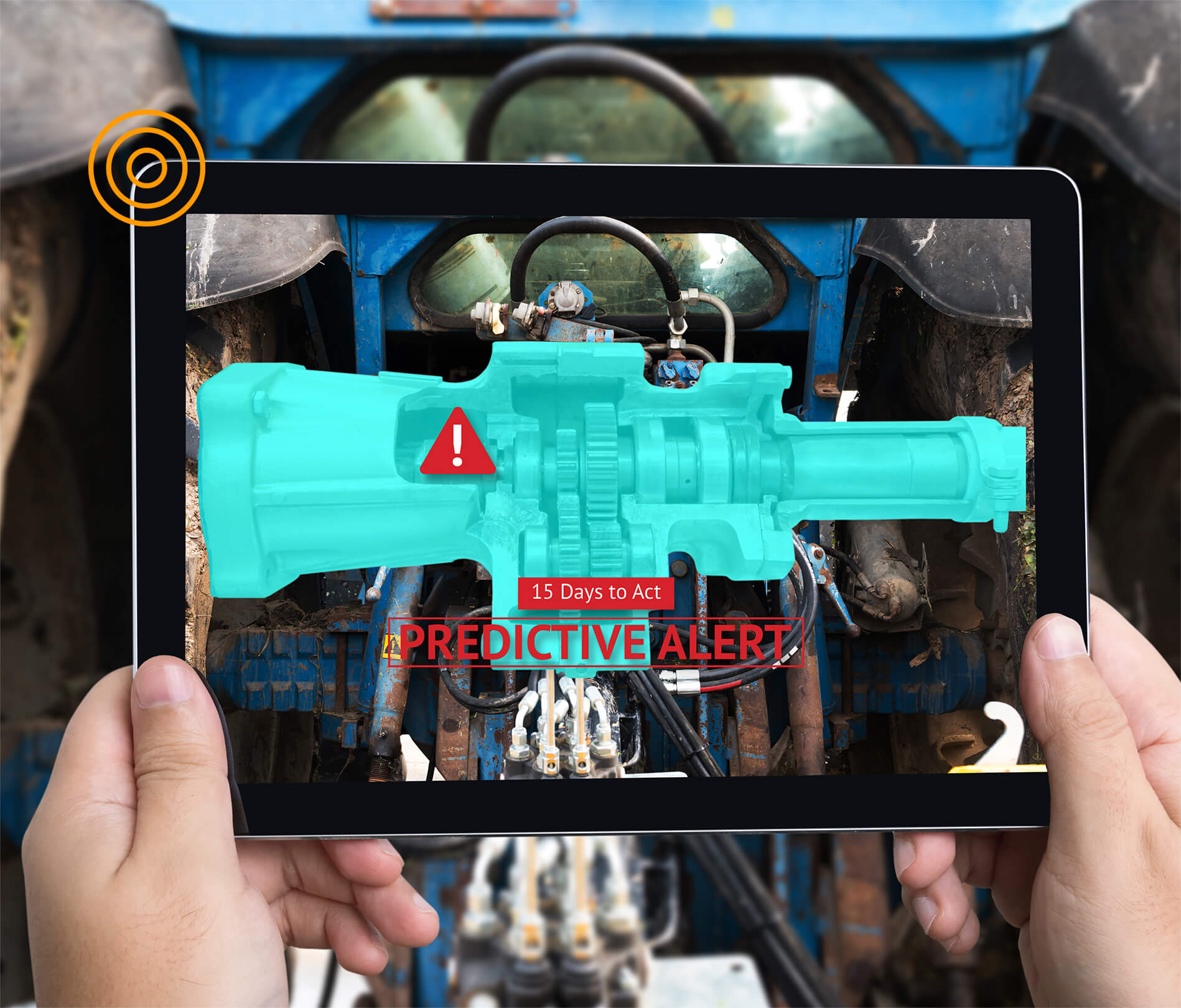
Predictive maintenance the maintenance of the future
Large amounts of data (BigData) are stored and evaluated to calculate the ideal time for maintenance. Service team assignments are optimized, maintenance and service intervals as well as spare parts management are better organized. Machine output and plant productivity are increased. Example: The sensors of a system report too strong vibrations. The affected component is renewed at a proposed time to prevent failure. An intelligent spare parts warehouse automatically orders the replacement article at the right time and place.
The service employee who is in the vicinity on the calculated delivery date receives all relevant data as an order. Or: If it makes sense, replacement during the next plant shutdown is recommended. In addition, wearing parts can often be used beyond the manufacturer’s specifications. In this way, predictive maintenance enables the reduction of maintenance costs.
What does this mean for the control room?
If operator intervention is necessary, the operator will receive much more meaningful information than was previously possible. This assists him to react more purposefully and confidently, especially in stressful situations.
Get advice now!

Get advice now!
A completely restructured energy market with new business models
The energy turnaround will lead to more small, decentralized power generation plants. The development of intelligent networks (smart grids) and intelligent electricity meters (smart meters) links all those involved in the energy system: energy producers, storage and network operators and consumers. These should make it possible to reduce demand during periods of high consumption, contribute to better network utilization and security of supply. One possibility: The washing machine starts automatically at night when the electricity price is lower. At the same time, consumption peaks and power fluctuations in the grid are minimized in this way. Or the electric car feeds electricity into the household or regional grid. By linking to the electronic calendars of the vehicle owners, the system recognizes how much remaining capacity must remain in the battery for the next trips.
What does this mean for the control room?
The entire industry will offer new services for its customers, which will be billed according to performance. It goes without saying that the availability of the service must be monitored again and must function almost without interruption. The consequence: control rooms become larger. The number of control rooms is increasing.
Get advice now!

Get advice now!
Electromobility: maximum networking for more safety – even without control
Two “cars” passing each other at a speed of more than ten km/h without producing an accident? Hardly conceivable in the early years of automotive engineering. Today motorists meet each other on the highways at 200 km/h. It’s nothing special anymore. Like the people at the end of the 19th century, we are at a crossroads again today. We are breaking new ground with electromobility. This is not only about highly complex electric motors, but also about creating autonomous means of transport that use thousands of sensors to ensure maximum safety. “…in future, the steering wheel in a car will be an optional extra,” predicts Elon Musk, one of the pioneers of electric mobility, in an interview in 2016.
What does this mean for the control room?
Maybe in the future we can actually do without motorists, but not without people who coordinate traffic. Sensors and actuators in the vehicles, lanes, traffic lights, charging stations, etc. must be understood and controlled. Control rooms in the traffic sector expect a wealth of tasks. There, incoming data from various sources must be evaluated and processed.
Get advice now!

Get advice now!
Complex IT security, with defense strategies against hackers and malware
IT security systems that are becoming increasingly complex must be kept up to date. Permanent observation and monitoring as well as real-time data evaluation are among the central requirements. Almost all business processes of a company are based on TCP-IP communication via the Internet. A technology that offers considerable advantages for the communication between systems. The other side of the coin: interfaces and “open doors” through which hackers & malware can access and damage systems.
What does this mean for the control room?
The SOC (Security Operation Center) is required to monitor internal and external threats (intrusion detection & extrusion detection). To achieve this, all the company’s security systems must be kept homogeneously up to date. In the case of acute threats, it is important to act immediately and not to lose time. In the SOC, specialists come together to develop joint defense strategies. In CI companies, it also functions as SPoC (Single Point of Contact) and involves, for example, the press office and company management. Even more than in the past, all threads of communication will converge here in the future.
Why a new control room? And why with JST?
Are you planning to “redesign” your control room? Or are you planning a completely new control room from the ground up? In both cases, we are talking about a significant investment and a decision that sets the course for the future – you are choosing a partner who will accompany you and your team throughout the control room lifecycle for the next ten to fifteen years. At this point, we would like to introduce ourselves as your partner in this collaboration and share some key facts with you: Why are we the right partner for your project?
79
%
In 79% of the projects, the external perception of the control room could be improved.
87
%
87% of control rooms in the service sector were able to use the control room as a sales tool and thereby increase their revenues both internally and externally.
84
%
In 84% of projects using JST technology, the number of large-screen displays and workstation monitors could be reduced.
93
%
100
%
In 100% of the projects, workplace ergonomics and the employees’ subjective well-being in the control room were improved. As a result, there is higher motivation within the team and fewer physical complaints and sick leave notifications.
Our motto: We think of everything!
We support you through every phase of the project
Free and non-binding consultation
You’re planning changes in your control room? We offer the full range of technical and ergonomic solutions. Take advantage of our tailored consulting services – or visit us directly in Europe’s most advanced control room simulator!
Planning and photorealistic room visualisation
With architect-compliant room planning and free potential analyses, we provide tailored solutions for your requirements. Would you like to experience your new control room even before it is built? Video simulations and 3D renderings make it possible.
Project management and installation
Operation and service of your control room
“Keep the systems running!” – we’re there for you even after the installation has been completed. You decide to what extent we support you – from basic service to full support for your system. Knowledge transfer to ensure the long-term operation of your control room technology.
JST product overview: thinking of everything!
COSTS: NO SURPRISES THANKS TO BKS!
You receive a BKS – what’s behind it?
To support you as efficiently as possible in your project, we are always transparent about prices. This prevents misunderstandings and ensures that, from the very beginning, you know what budget you should plan for.
You can easily make complete deletions, change quantities or add components yourself in a BKS Excel table. This way, you can immediately see what impact any changes during the course of the project will have on your overall budget. We are happy to review the BKS after your changes to check it for accuracy and, in particular, technical feasibility, so that your self-prepared cost estimate remains reliable.
The BKS is not a rough budget plan – it is a truly robust cost estimate that you can genuinely rely on in the further phases of the project.